

Admin 11 Nov 2025
The cement manufacturing industry plays a vital role in the infrastructure development of every nation. From buildings and bridges to highways and dams, cement serves as the foundation for countless construction projects. Among the various components used in the cement production process, the rotary kiln stands out as one of the most critical pieces of equipment. It is the heart of the cement plant — where raw materials are transformed into clinker, the key ingredient in cement.
A rotary kiln is a long, cylindrical, slightly inclined furnace that rotates slowly around its axis. It is designed to heat raw materials to very high temperatures, typically between 1400°C and 1500°C, to bring about a series of physical and chemical reactions that convert raw meal into clinker — the semi-finished material used to produce cement.
The kiln is made from high-quality steel and lined with refractory bricks to withstand extreme heat. The design allows for continuous material flow, making the rotary kiln one of the most efficient and durable systems in cement manufacturing.
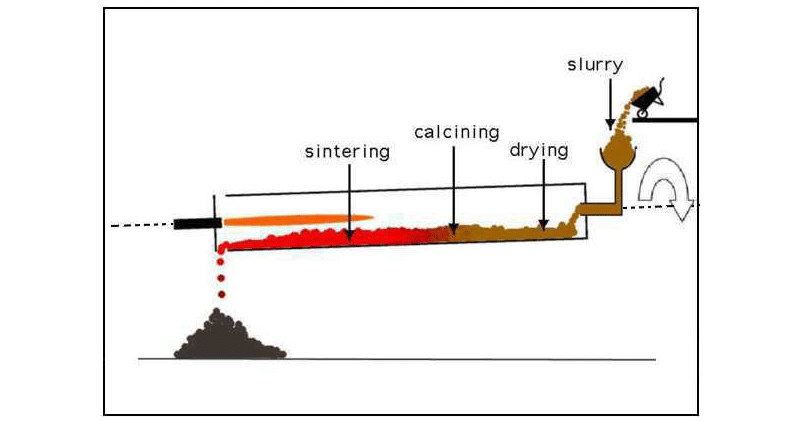
The rotary kiln operates on a simple yet highly effective principle — continuous heat transfer through rotation. Here’s how it works step by step:
1. Raw Material Feeding:
The raw mix, also known as kiln feed, is introduced from the upper end of the kiln. This mixture usually contains limestone, clay, iron ore, and silica.
The cement industry has embraced innovation to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact. Some of the key advancements include:
2. Rotation and Incline:
The kiln is slightly inclined (1–4°) to facilitate the downward movement of materials as it rotates slowly, typically 0.5–5 revolutions per minute.
3. Heating and Reaction Zones:
4. Fuel and Combustion:
Rotary kilns use fuels such as coal, natural gas, oil, or alternative fuels. The heat generated ensures complete chemical transformation, ensuring high-quality clinker output.
The rotary kiln is more than just a heating device — it’s the core reactor in the cement manufacturing process. Here’s how it contributes to each stage:
The primary role of the rotary kiln is to transform raw materials into clinker through calcination and sintering. The high temperatures promote chemical reactions between calcium carbonate, silica, alumina, and iron oxide, producing the compounds that form cement.
Rotary kilns are engineered for optimal heat transfer. The counter-current flow of hot gases and raw materials ensures maximum energy utilization, reducing fuel consumption and production costs.
Modern rotary kilns are equipped with temperature sensors, gas analyzers, and computerized control systems that allow operators to maintain stable operating conditions. Consistent temperature control directly impacts the clinker quality, ensuring uniformity in cement performance.
The rotary kiln works seamlessly with other cement plant components like the preheater, precalciner, and clinker cooler. Together, they form an integrated system that improves efficiency, minimizes energy loss, and enhances productivity.
With increasing global demand for cement and growing environmental awareness, the future of rotary kilns is focused on efficiency, automation, and sustainability. Manufacturers are investing in research to develop carbon-neutral kilns using hydrogen or electric heating technologies.